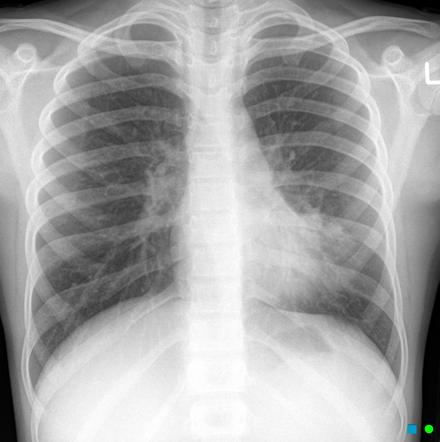
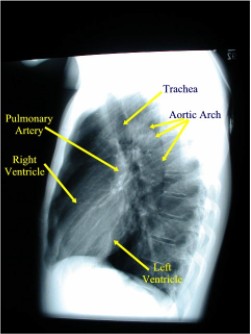
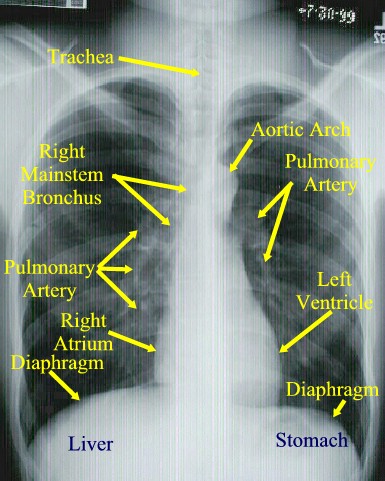
Retrocardiac Air Space Disease
Retrocardiac air space disease. Airspace disease is considered chronic when it persists beyond 4-6 weeks after treatment. Tendency to coalesce near hila. The margins of airspace disease are fuzzy and indistinct.
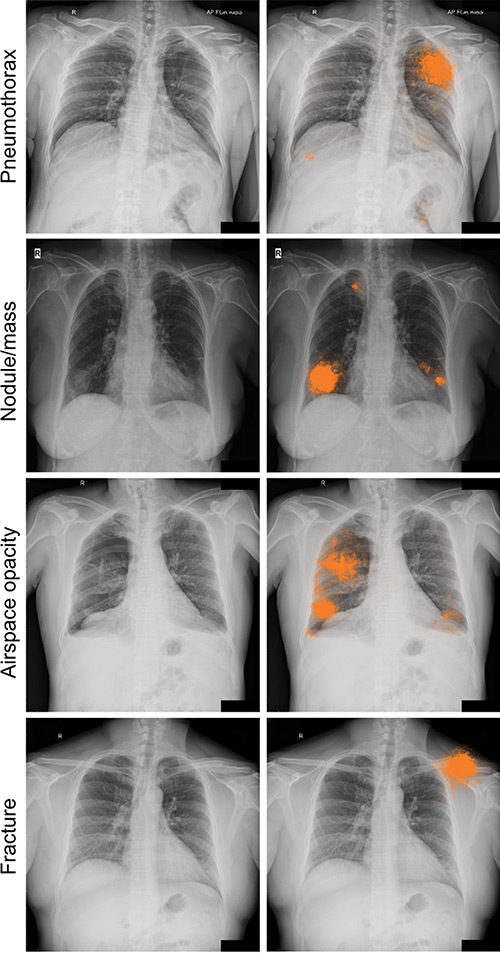
Air-space opacification is a descriptive term that refers to filling of the lung parenchyma with material that attenuates x-rays more than the unaffected surrounding lung tissue. Consolidation or ground-glass opacity occurs when alveolar air is replaced by fluid pus blood cells or other material. Test results for infl uenza virus respiratory fl uorescent antibodies D3 Ultra DFA Respiratory Virus Screening and In-fectious Disease Kit.
Air cant get through the consolidation so your lung cant do its job of bringing in fresh air and removing the air your body has used. The location retrocardiac - behind the heart shouldnt make a difference. Identifying multifocal air-space disease on CXR can be a significant clue to COVID-19 pneumonia.
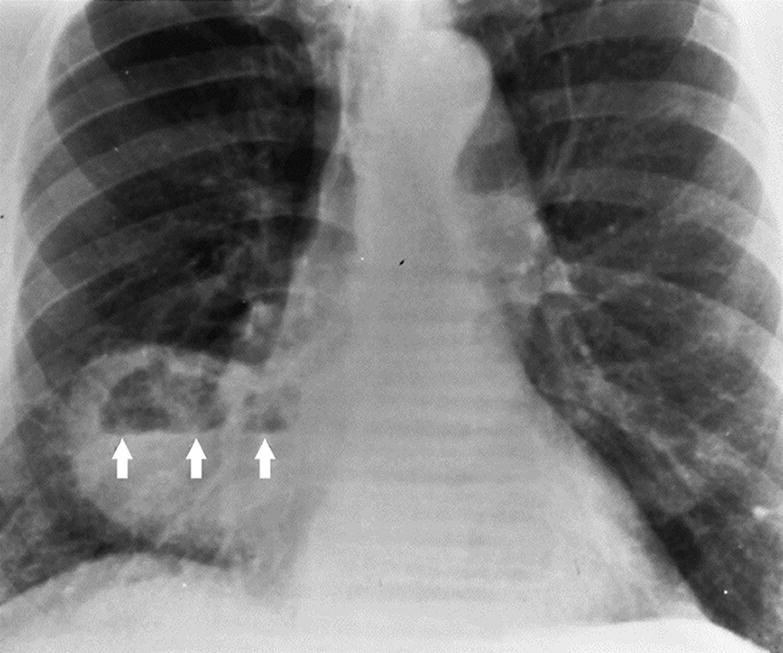
By early detection and proper evaluation of the abnormal retrocardiac shadows the radiologist may establish the diagnosis before the clinical signs and symptoms of compression of large blood vessels and nerves become. Retrocardiac Air Space Disease. Air space opacification is a descriptive term that refers to filling of the pulmonary tree with material that attenuates x-rays more than the surrounding lung parenchyma.
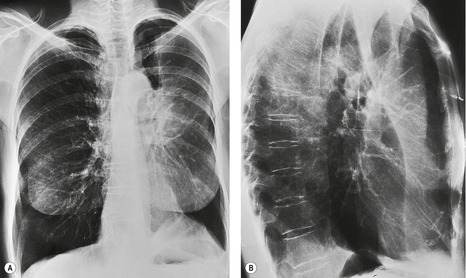
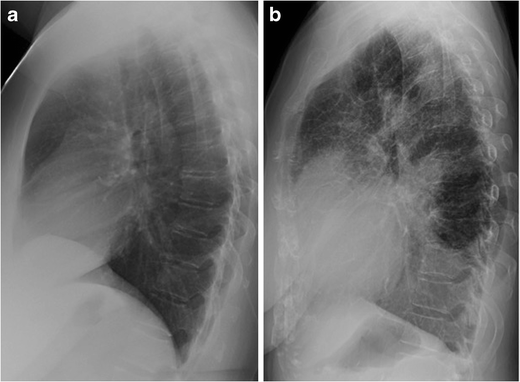
This unusual type of bibasilar atelectasis happens when the lung is trapped as a result of pleural disease while being devoid of air. The opacities tend to be confluent merging into one another. These represent air-space or acinar nodules.
Patchy diffuse air space consolidation. Diagnostic Hy-brids Inc Athens OH USA and virus culture were negative. There are a number of different causes of insult to the alveoli including build up of fluid hemorrhage infection malignancy and build up of protein and mineral deposits.
It is one of the many patterns of lung opacification and is equivalent to the pathological diagnosis of pulmonary consolidation. The latter will often reveal air trapping on expiratory images 25-27.
Alveolar lung diseases are classified as processes that affect these units that ultimately lead to issues with ventilation.
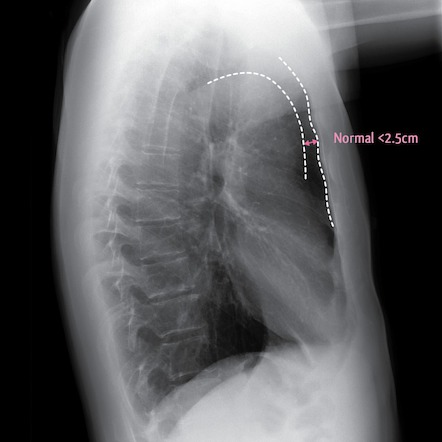
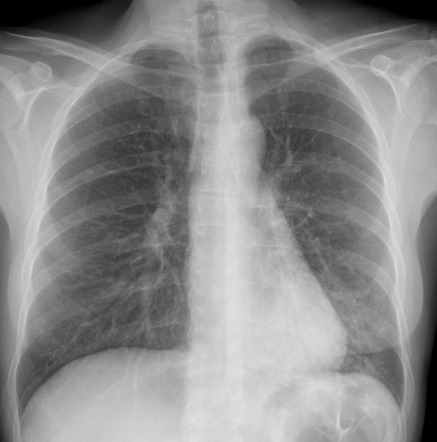
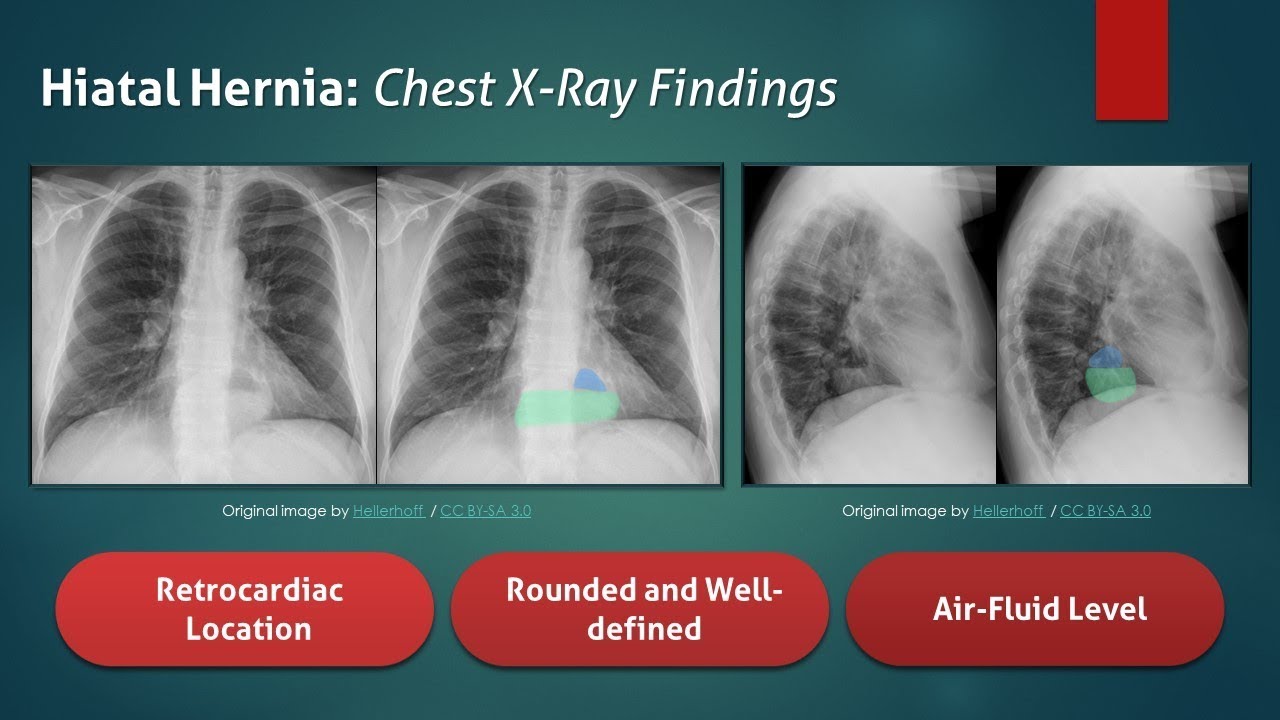
Airspace disease is considered chronic when it persists beyond 4-6 weeks after treatment. A single retrocardiac air-fluid level on a chest radiograph typically implies the presence of a sliding hiatal hernia. This unusual type of bibasilar atelectasis happens when the lung is trapped as a result of pleural disease while being devoid of air. Airspace disease also known as alveolar lung disease is a generic term thats used to describe abnormalities on chest x-ray or CT. The most common clinical causes of this CT pattern of disease include hypersensitivity pneumonitis sarcoidosis atypical infections eg those caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae with associated bronchiolitis and acute interstitial pneumonia 25. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM J984 became effective on October 1 2020. J984 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. And retrocardiac air space disease. Retrocardiac Air Space Disease.
The location retrocardiac - behind the heart shouldnt make a difference. It is the radiological correlate of the pathological diagnosis of pulmonary consolidation. The most common clinical causes of this CT pattern of disease include hypersensitivity pneumonitis sarcoidosis atypical infections eg those caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae with associated bronchiolitis and acute interstitial pneumonia 25. The particular way the lung collapses can often produce a. Acinar or air-space nodules. CT 5-mm slice thickness in a patient with bilateral consolidation. Tendency to coalesce near hila.
























Post a Comment for "Retrocardiac Air Space Disease"