Immunity Depends Upon The Production Of Disease-specific Antibodies To Destroy Harmful Bacteria.
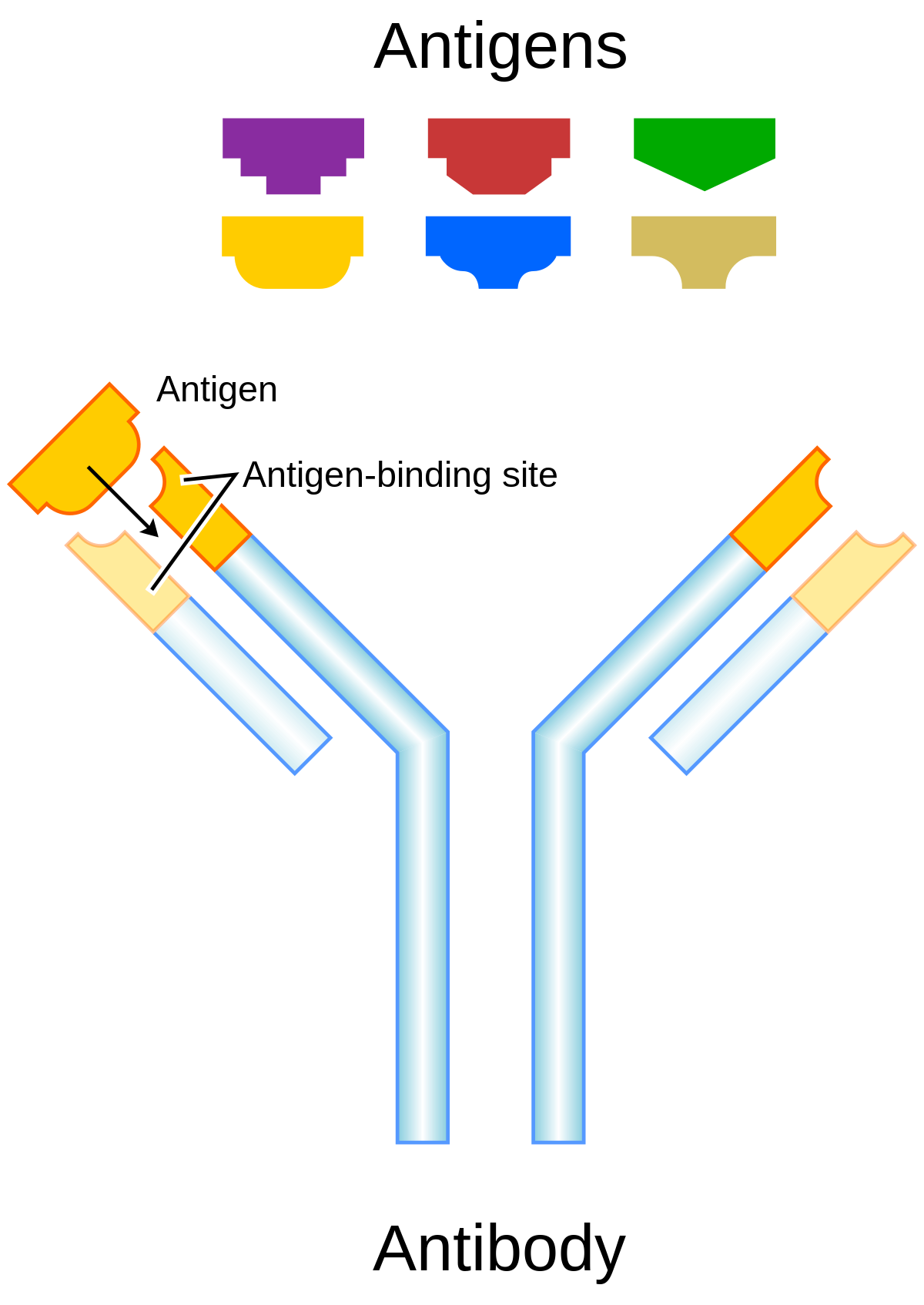
Immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria.. Both passive and active immunity have role in the elimination of bacteria and naturalization of toxins. An antibody Ab also known as an immunoglobulin Ig is a large Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. Extracellular bacteria G and G- induce inflammation and production of toxins.
Immunity to a disease is achieved through the presence of antibodies to that disease in a persons system. Immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria. Foreign substances such as viruses bacteria toxins and parasites are surrounded by antigensthat when introduced into the body are capable of inducing a response by the immune system.
Immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria. An interaction similar to a lock and key. Humoral Antibody-Mediated Immunity u Involves production of antibodies against foreign antigens.
The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the. Immune system protein. This is called immunity.
They are created by the immune system to fight germs and foreign substances. Play vital role in the immunity against most Specific antibody is particularly important of the helminthic infections and depend on in the control of extracellular parasites. Antibodies are proteins produced by the body to neutralize or destroy toxins or disease-carrying organisms.
Humoral immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria. Antibodies are compounds of protein and sugar that circulate in the bloodstream. Humoral immunity which takes place in the body fluids humors and is concerned with antibody and complement activities.
Humoral immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria. Immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria.
That is why with some diseases such as chickenpox you only get it once as the body has a chickenpox antibody stored ready and waiting to destroy it next time it arrives.
Foreign substances such as viruses bacteria toxins and parasites are surrounded by antigensthat when introduced into the body are capable of inducing a response by the immune system. There are many antibodies and each is specific for a particular type of antigen. Extracellular bacteria G and G- induce inflammation and production of toxins. Both passive and active immunity have role in the elimination of bacteria and naturalization of toxins. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the. Humoral immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria. Immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria. This neutralizes the intruders and attracts other immune system cells to help. Thus immune response in acquired immunity is due to the precise binding of antigens to antibody.
The the cytokines production by Th2 cells. Immune system protein. Humoral immunity How does active and passive immunity function. They are created by the immune system to fight germs and foreign substances. Antibodies can quickly detect germs and other potentially harmful substances and then attach to them. An interaction similar to a lock and key. Immunity depends upon the production of disease-specific antibodies to destroy harmful bacteria.
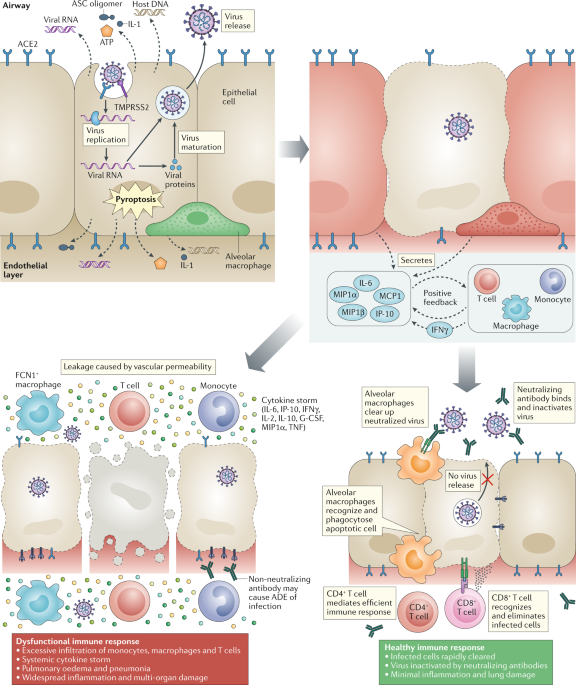
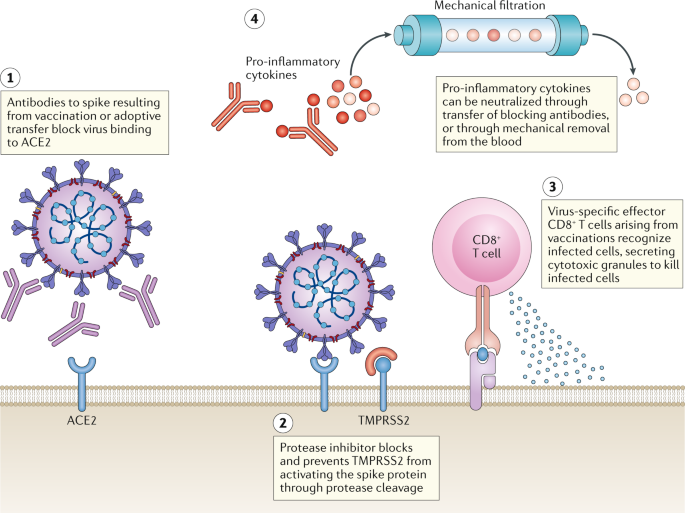
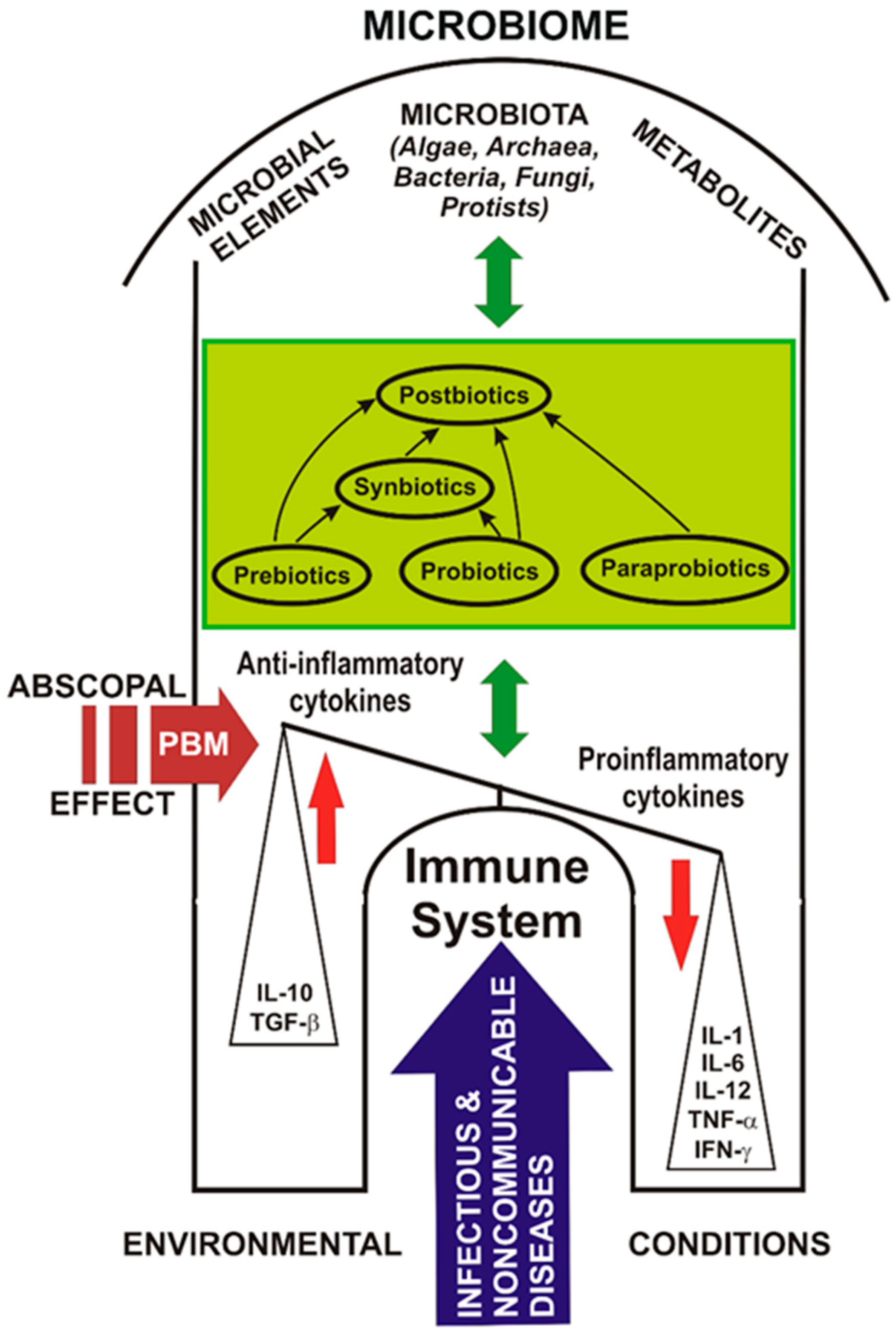
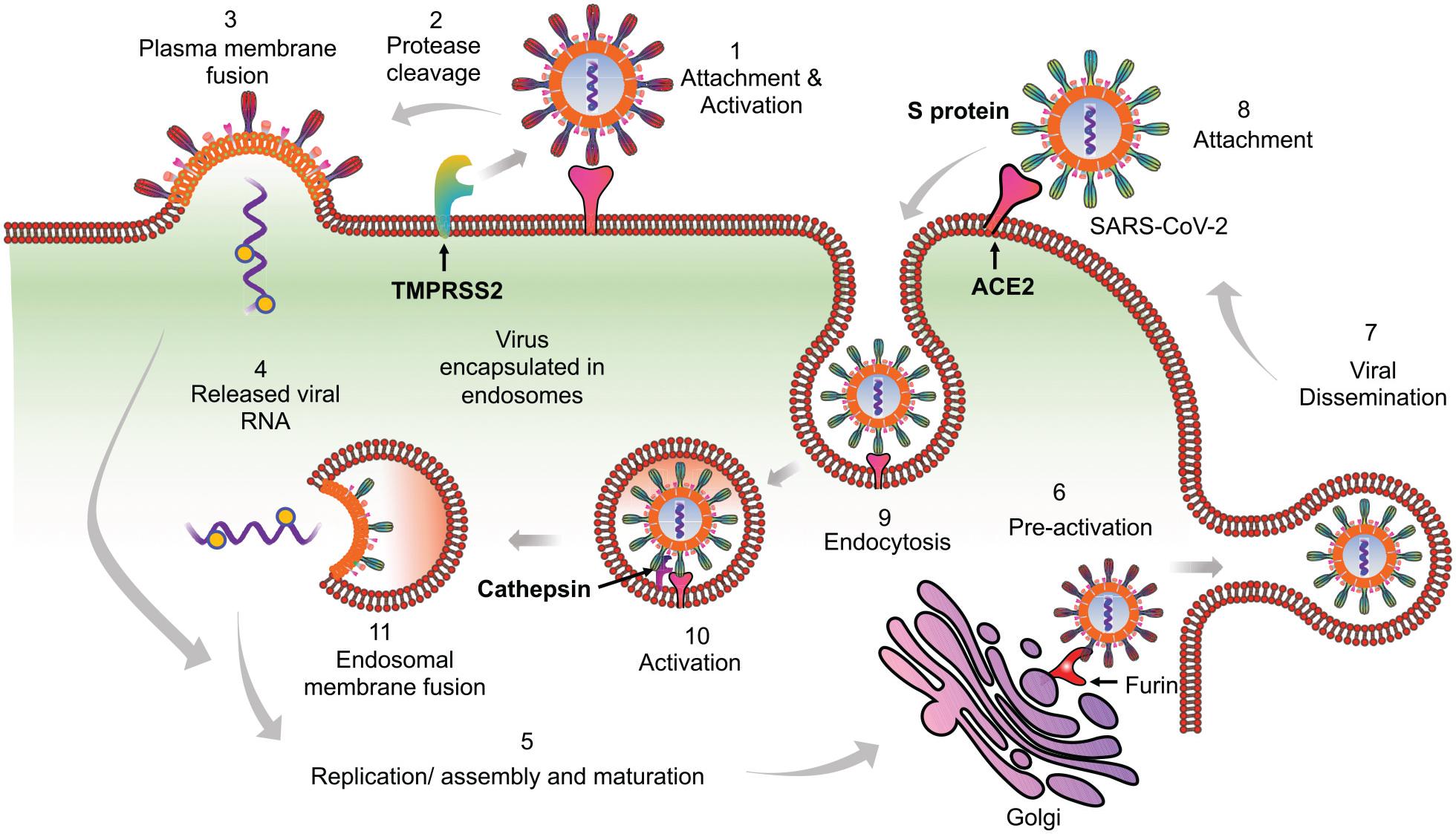


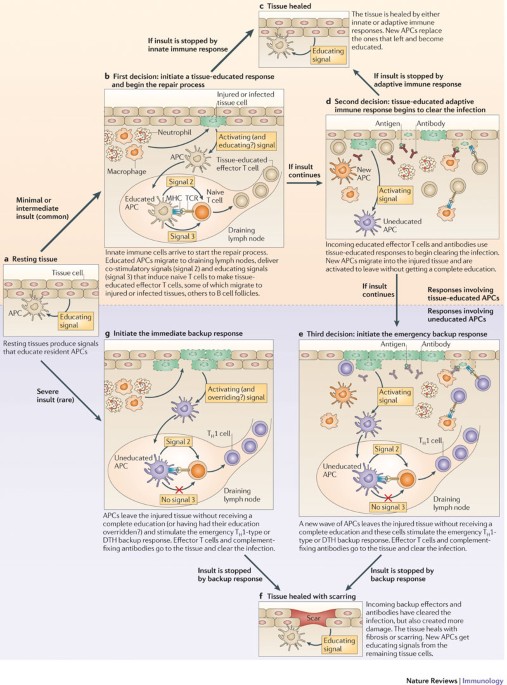
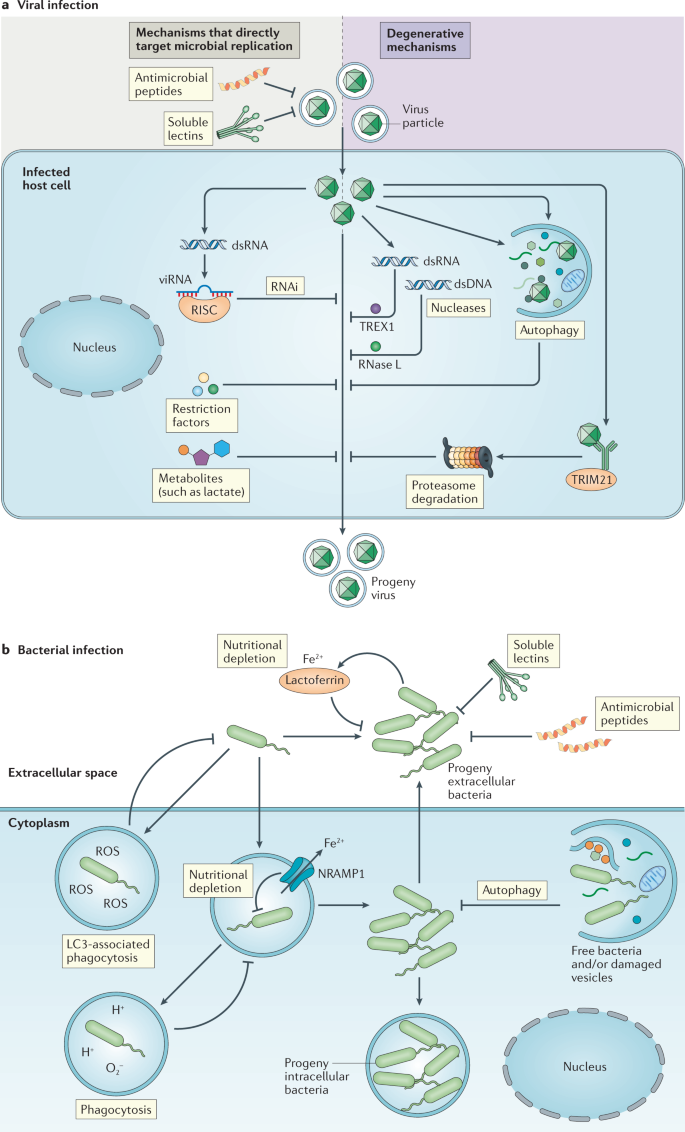

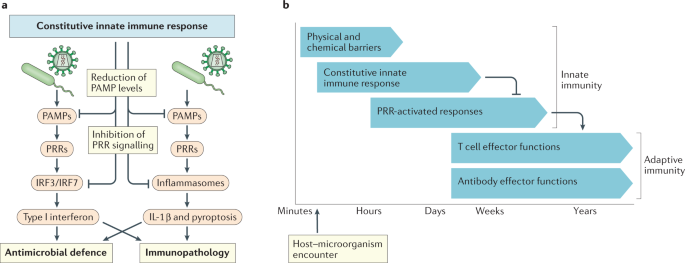
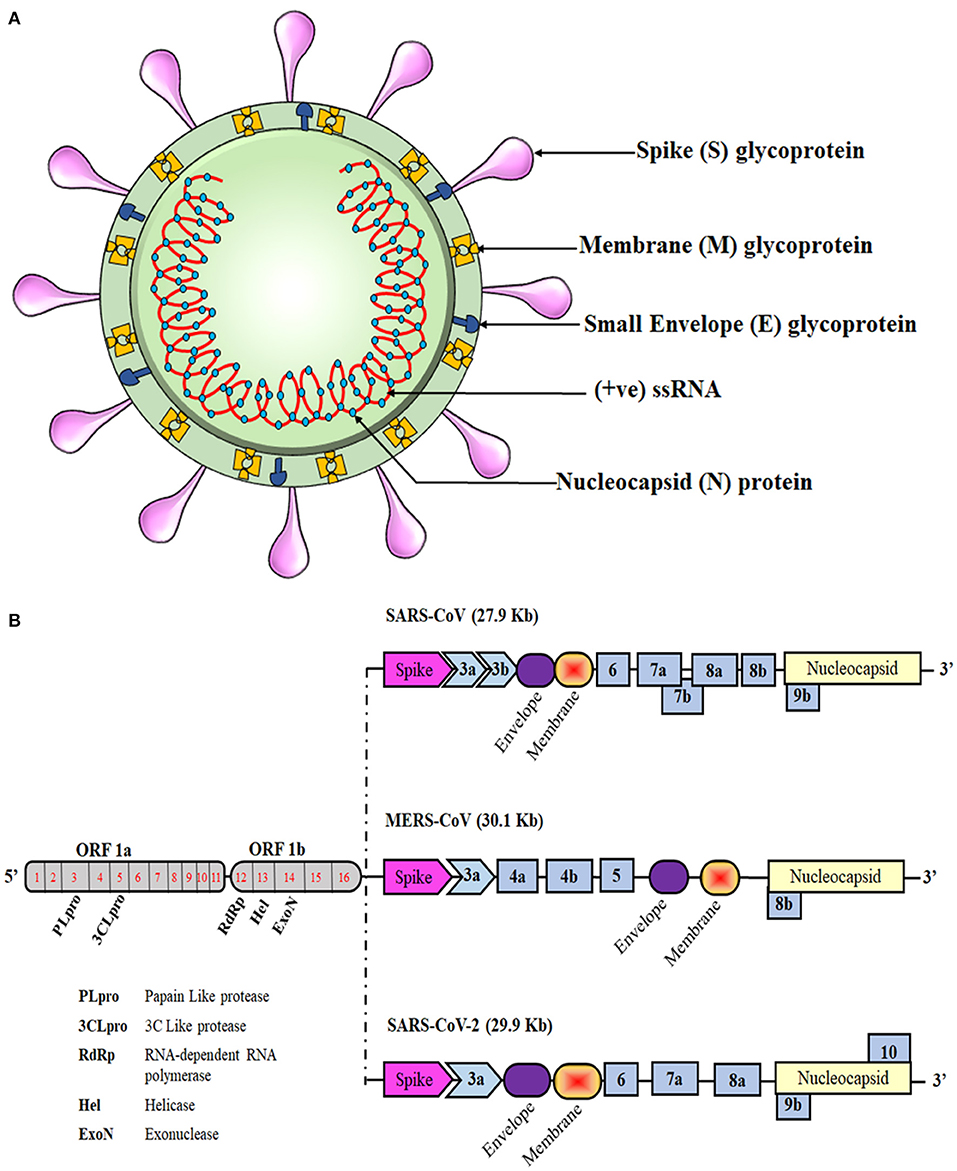
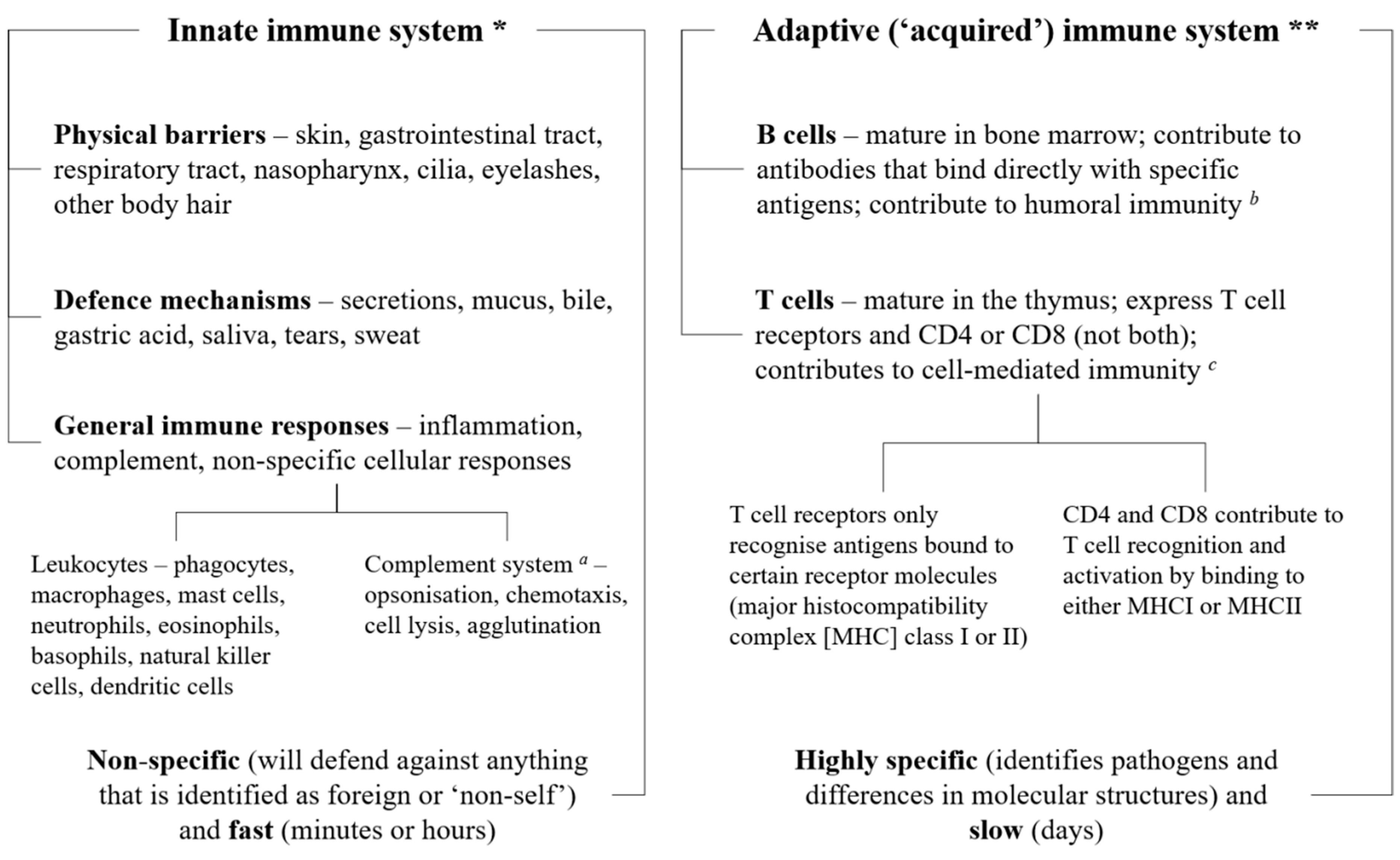
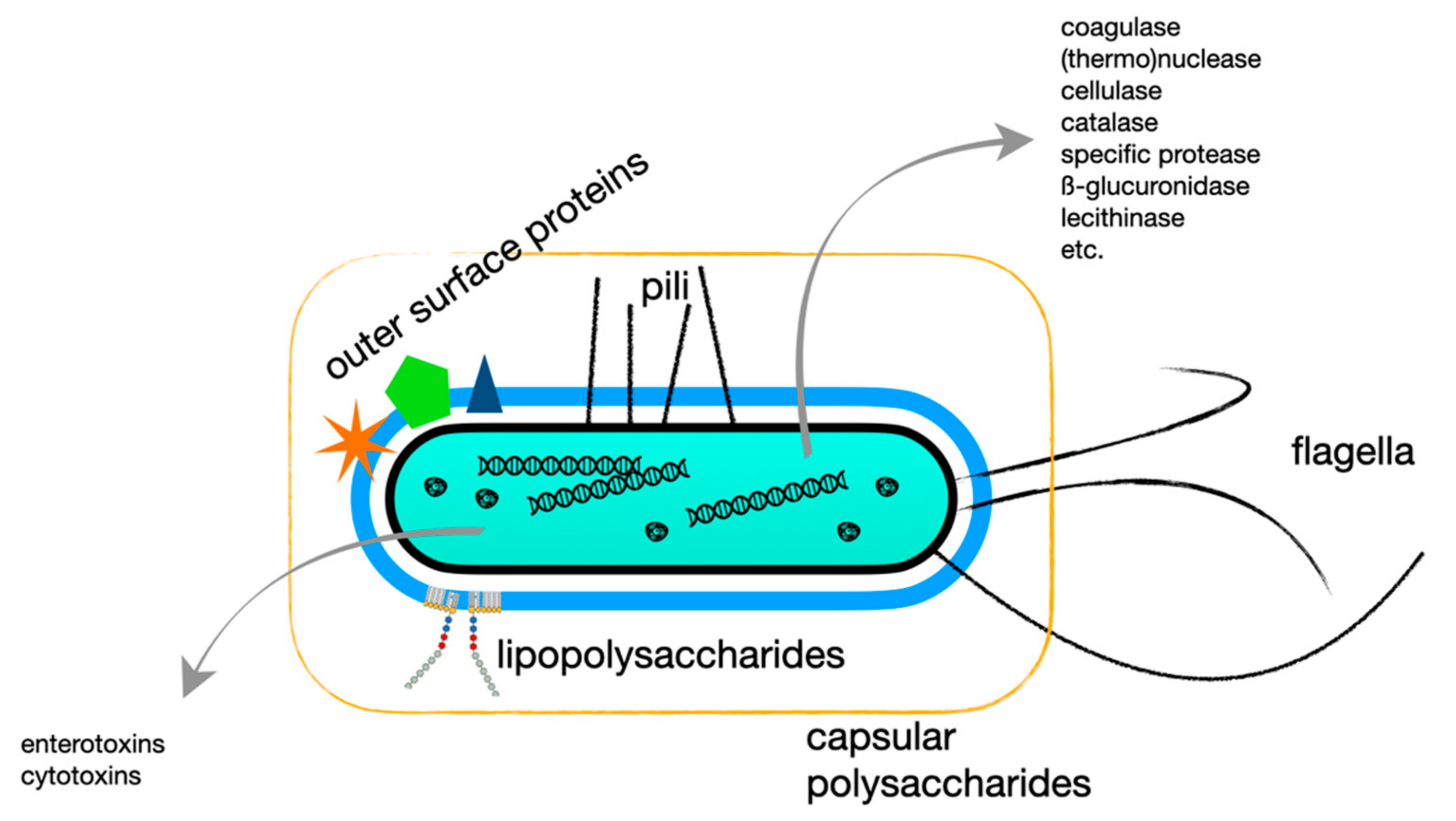

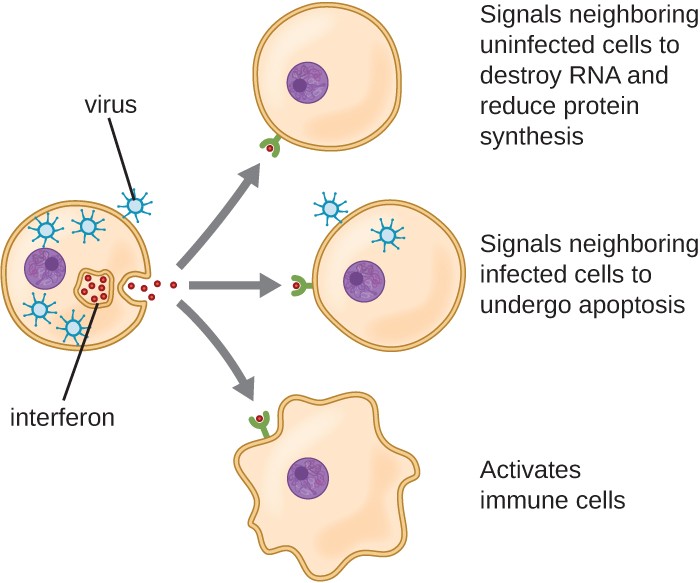
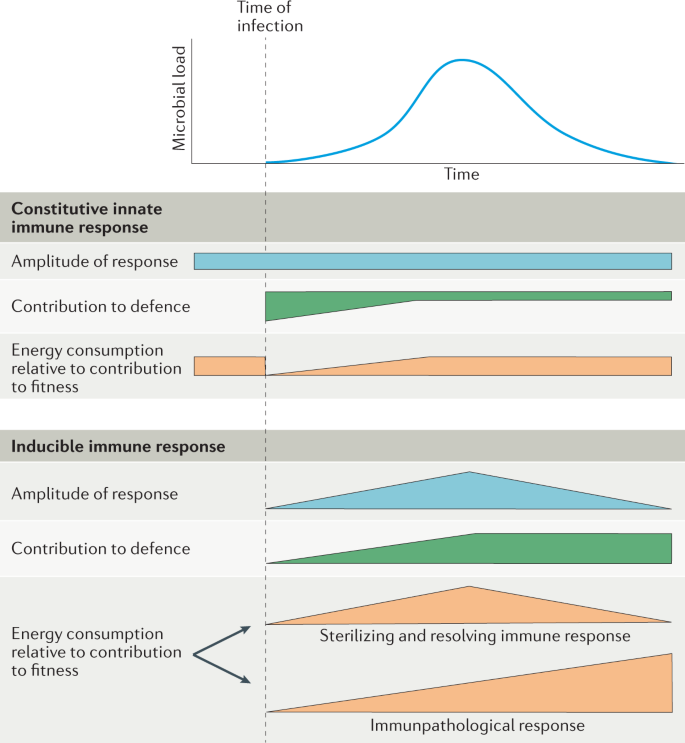
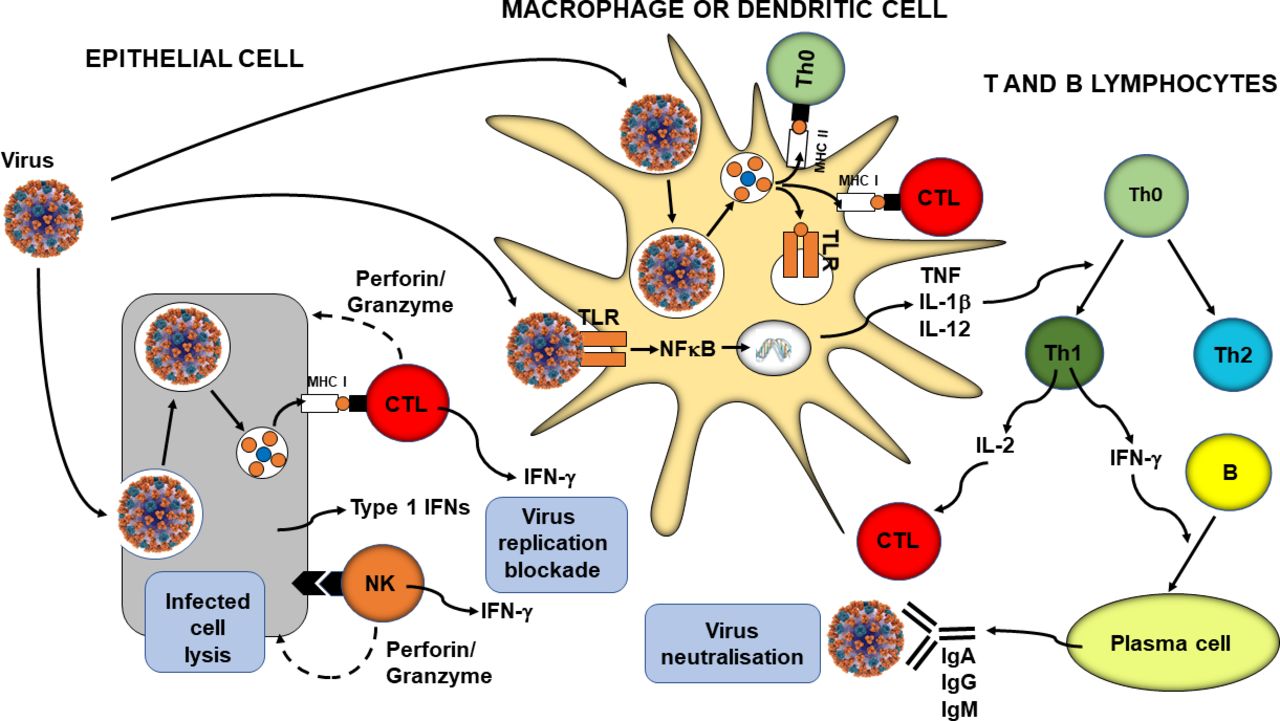

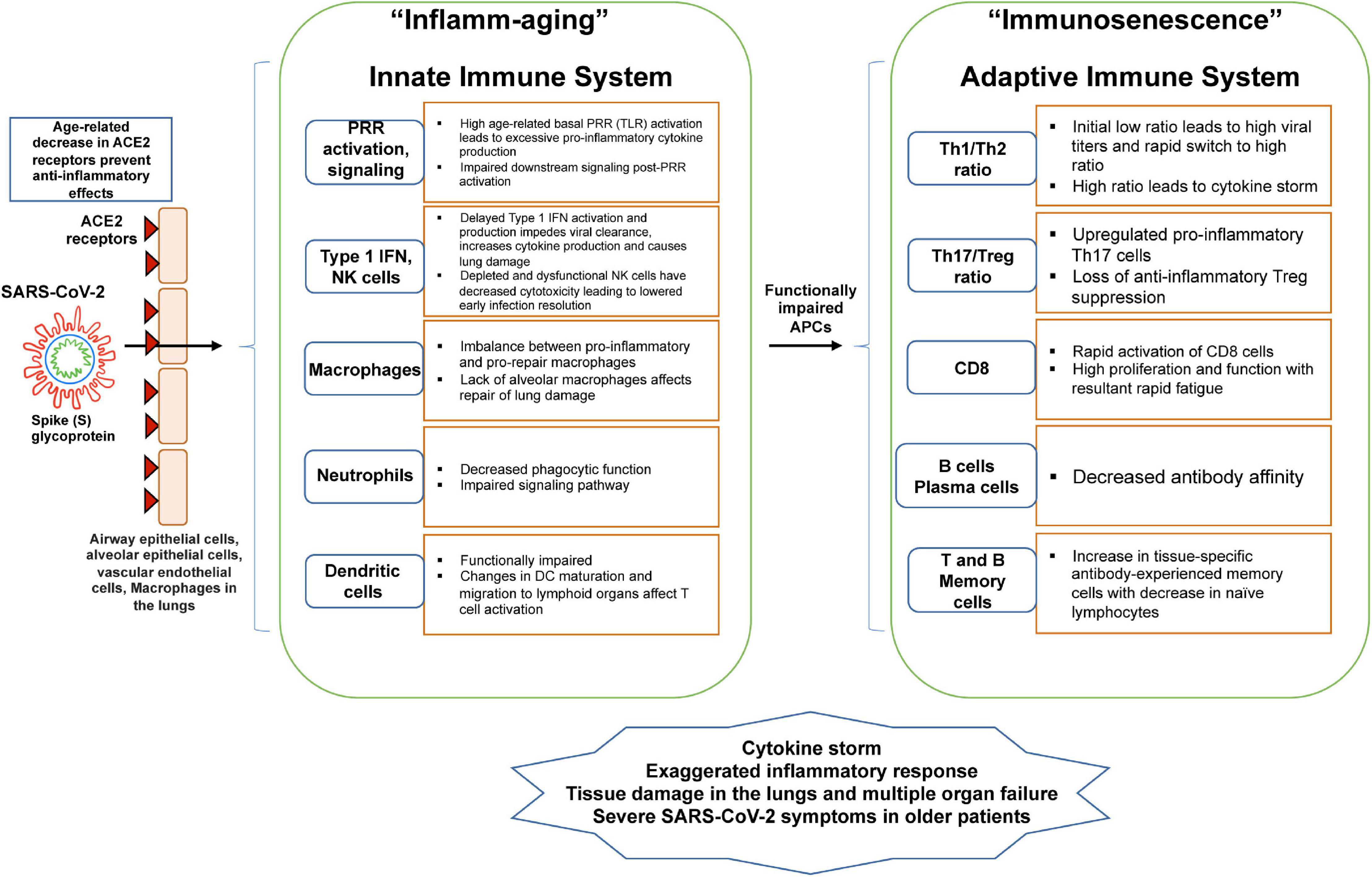
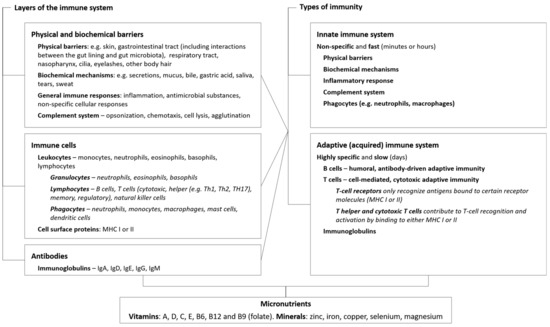
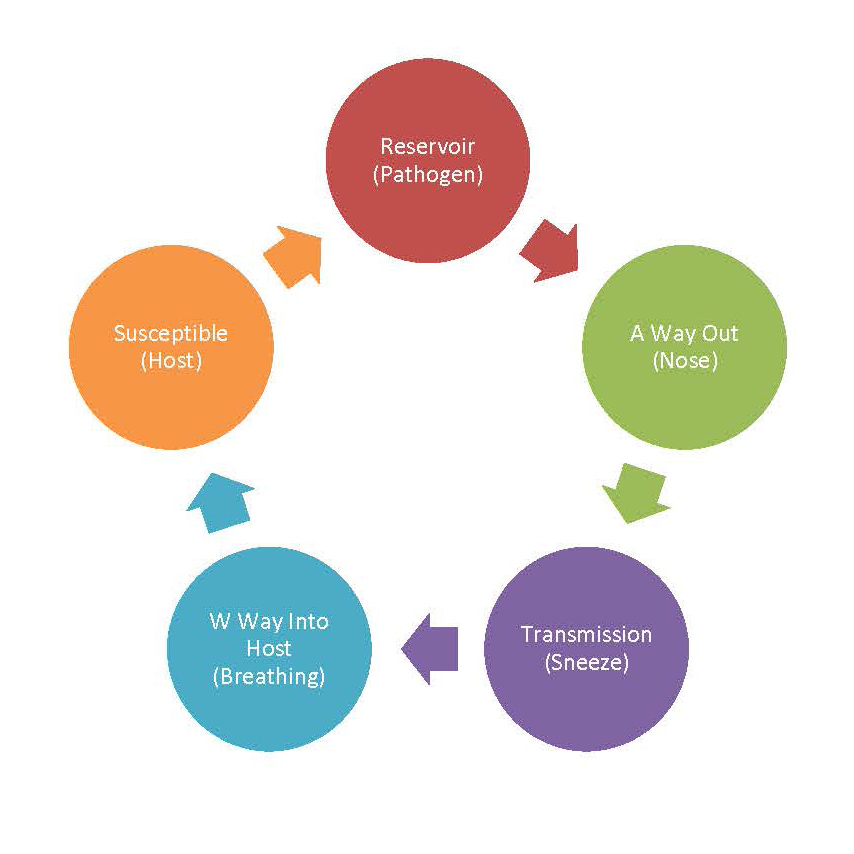





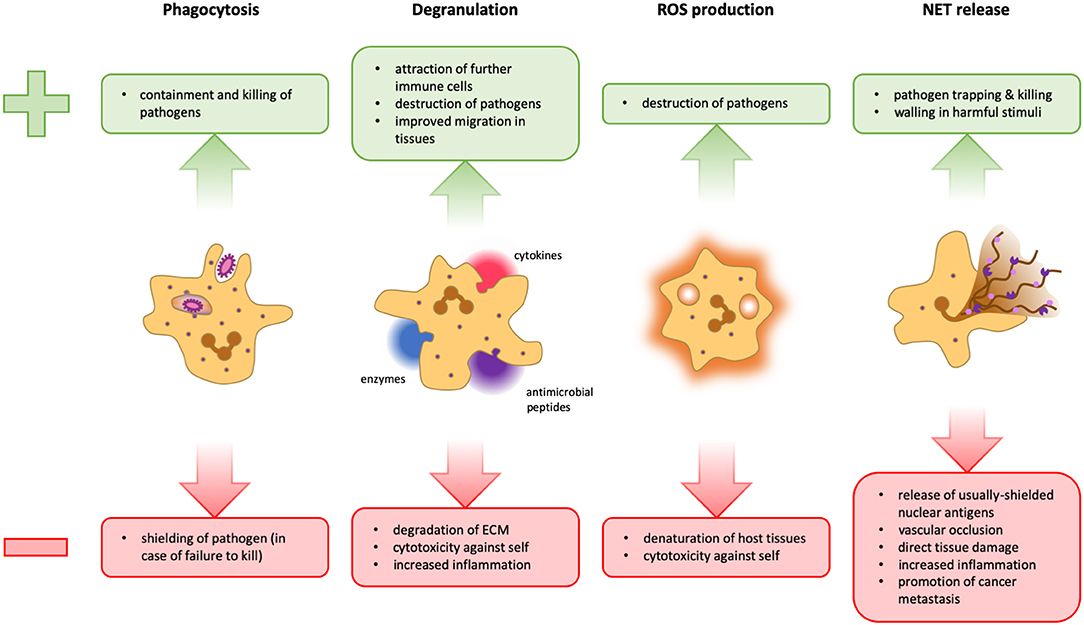
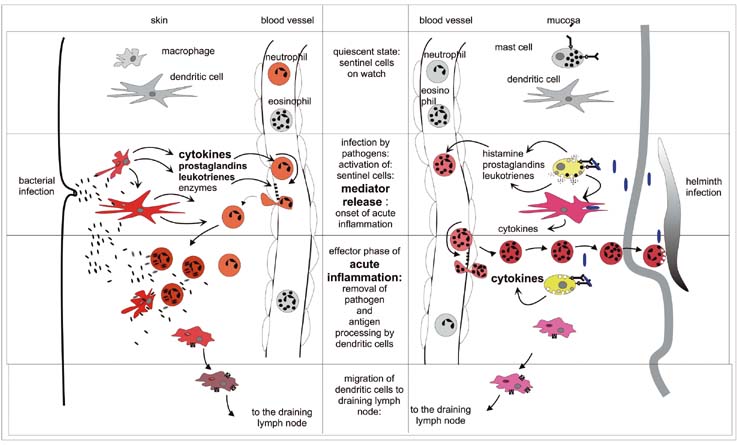
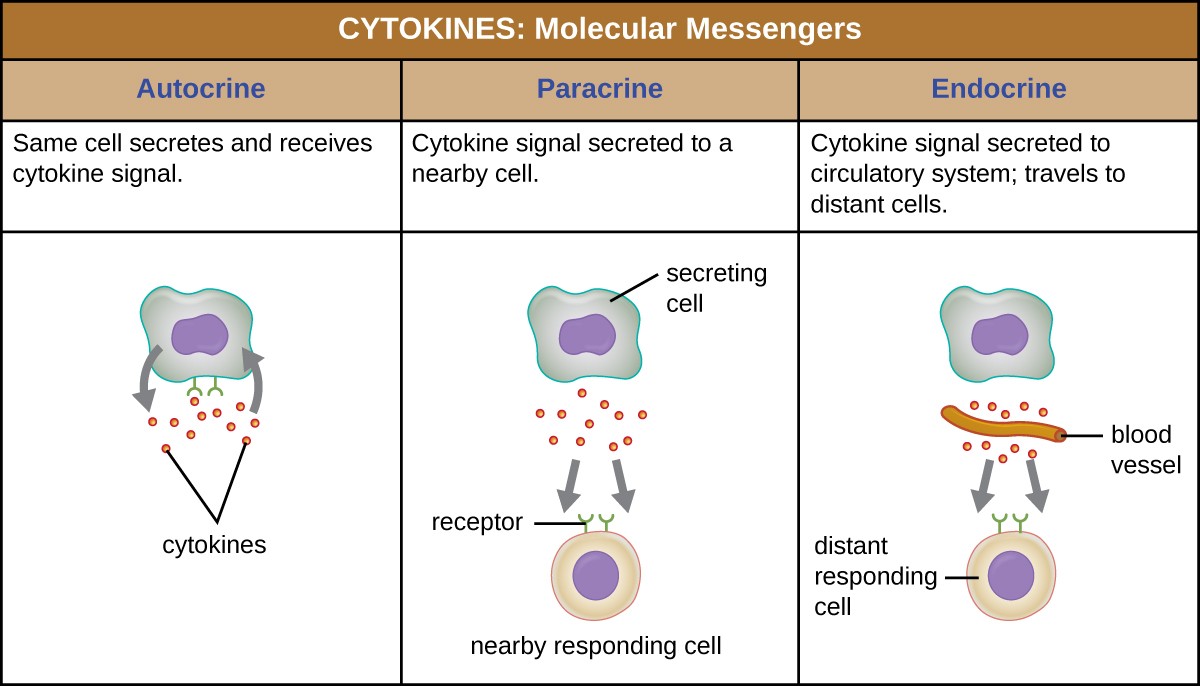

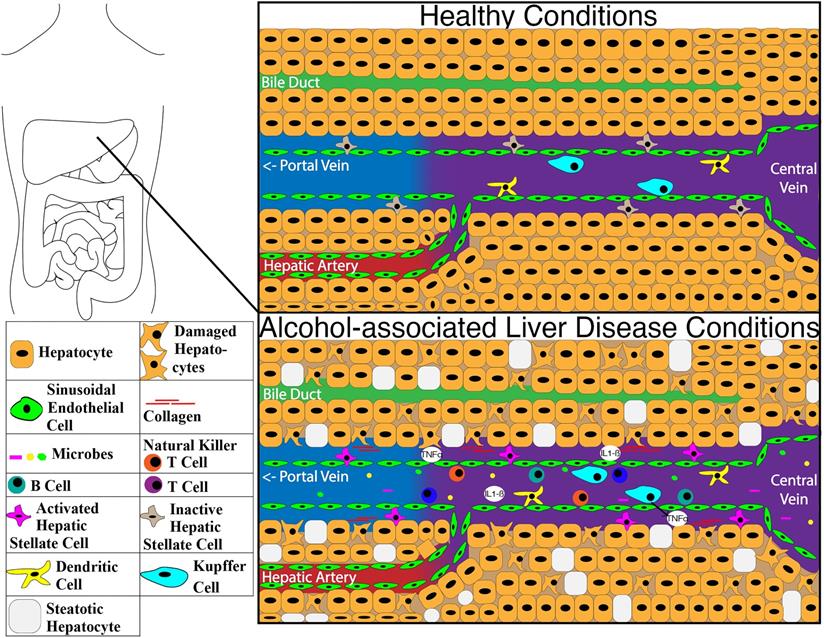
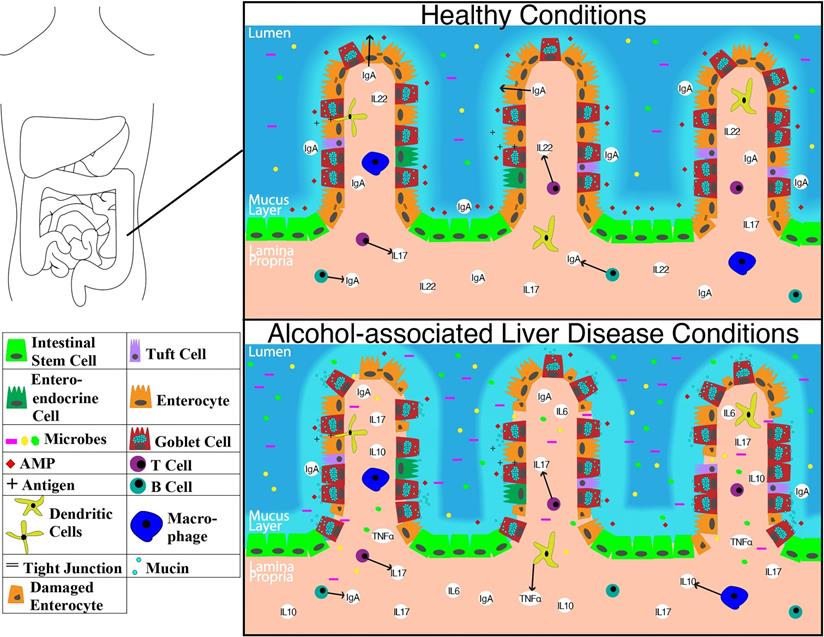
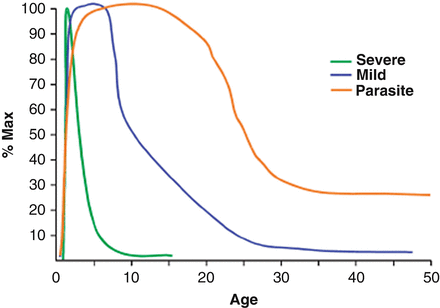

Post a Comment for "Immunity Depends Upon The Production Of Disease-specific Antibodies To Destroy Harmful Bacteria."