How Does Urine Osmolarity Compare Between The Two Treatment Groups?
How does urine osmolarity compare between the two treatment groups?. When the kidneys produce a urine more concentrated than 300mOsmL they are excreting more solutes compared to water than exists in the ECF which acts to dilute the ECF and thus lower its osmolarity. For dilute solutions the difference between osmolarity and osmolality is insignificant. How Does Urine PPT.
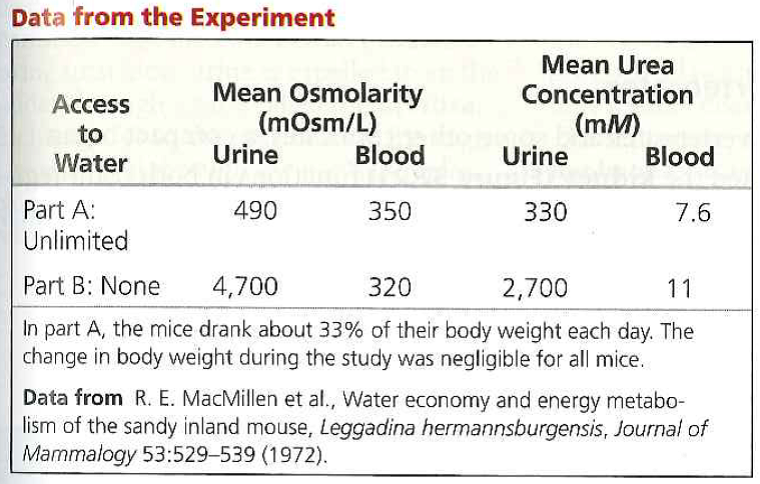
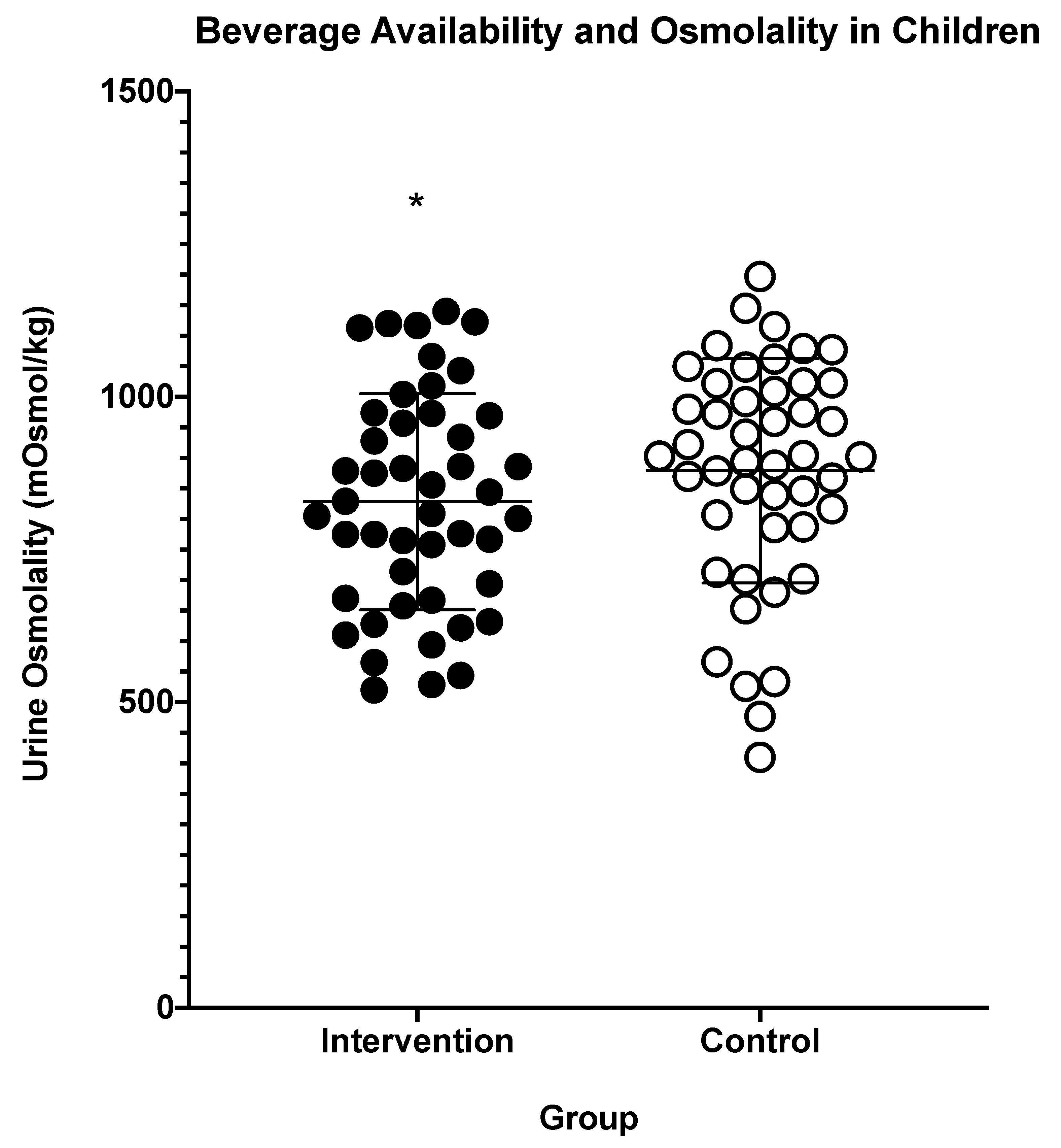
A Urine osmolarity is much higher in the mice. How does urine osmolarity compare between the two treatment groups. A Urine osmolarity is much higher in the mice.
Urinary osmolality in humans can range from around 50 to 1200 mOsm kg depending on whether the person has recently drunk large amounts of water lower amounts or has been without water for a long time higher. Stool osmolality - this may help evaluate chronic diarrhoea that does not appear to be due to a bacterial or parasitical infection ie. Presentation Summary.
How does urine osmolarity compare between the two treatment groups. One mole of a nondissociating substance eg glucose or urea dissolved in 1 kg of water decreases the freezing point of the resultant solution by 186 C. It also helps your doctor diagnose certain problems.
The Table Shows The Data From The Experiment. 14 OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR. A normal urine-to-serum ratio is approximately 02 to 47 for random samples and greater than 30 for first-morning samples dehydration normally occurs overnight.
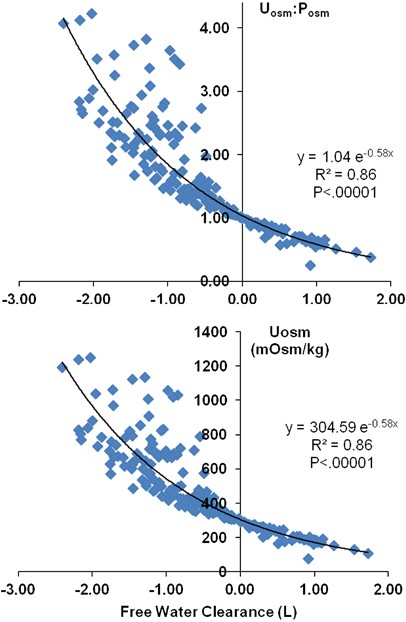
Such a solution has an osmolality of 1 Osmkg or 1000 mOsmkg. This video series is best watched from the start. ECF Osmolarity Urine Osmolarity and ADH The extracellular fluid has a normal osmolarity of 300mOsmL.
For mice with unlimited access to water what is the ratio of urine osmolarity to blood osmolarity. Biology 0 1452 users searched for this homework answer last month and 97 are doing it now lets get your homework done.
The table shows the data from the experiment.
One mole of a nondissociating substance eg glucose or urea dissolved in 1 kg of water decreases the freezing point of the resultant solution by 186 C. The table shows the data from the experiment. Measurements of osmolarity are temperature dependent because the volume of solvent varies with temperature ie. Part of our series on hyponatraemia - where we tackle the causes of low sodium using a systematic approach. This video series is best watched from the start. In close comparisons external fertilization often yields more offspring than does internal fertilization but internal fertilization offers the advantage that the smaller number of offspring produced often receive a greater amount of parental investment and a high probability of survival. A Urine osmolarity is much higher in the mice. How does urine osmolarity compare between the two treatment groups. Biology 0 1452 users searched for this homework answer last month and 97 are doing it now lets get your homework done.
For mice with unlimited access to water what is the ratio of urine osmolarity to blood osmolarity. Urinary osmolality in humans can range from around 50 to 1200 mOsm kg depending on whether the person has recently drunk large amounts of water lower amounts or has been without water for a long time higher. In healthy humans with limited fluid intake urine osmolality must be greater than 800 mOsm kg while 24-hour urine osmolality must average between 500 and 800 mOsm kg. Urine osmolality is a marker for how well the kidneys are working. Biology 0 1452 users searched for this homework answer last month and 97 are doing it now lets get your homework done. Examples of conditions that can cause increased urine osmolality include. When the kidneys produce a urine more concentrated than 300mOsmL they are excreting more solutes compared to water than exists in the ECF which acts to dilute the ECF and thus lower its osmolarity.





































Post a Comment for "How Does Urine Osmolarity Compare Between The Two Treatment Groups?"