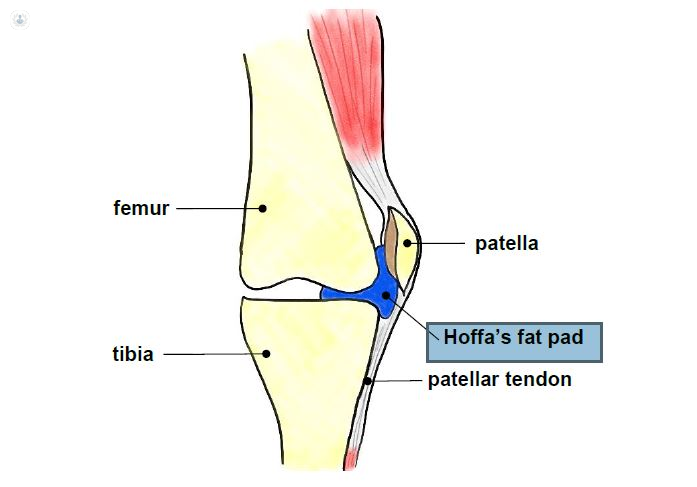
Suprapatellar Fat Pad Impingement Syndrome
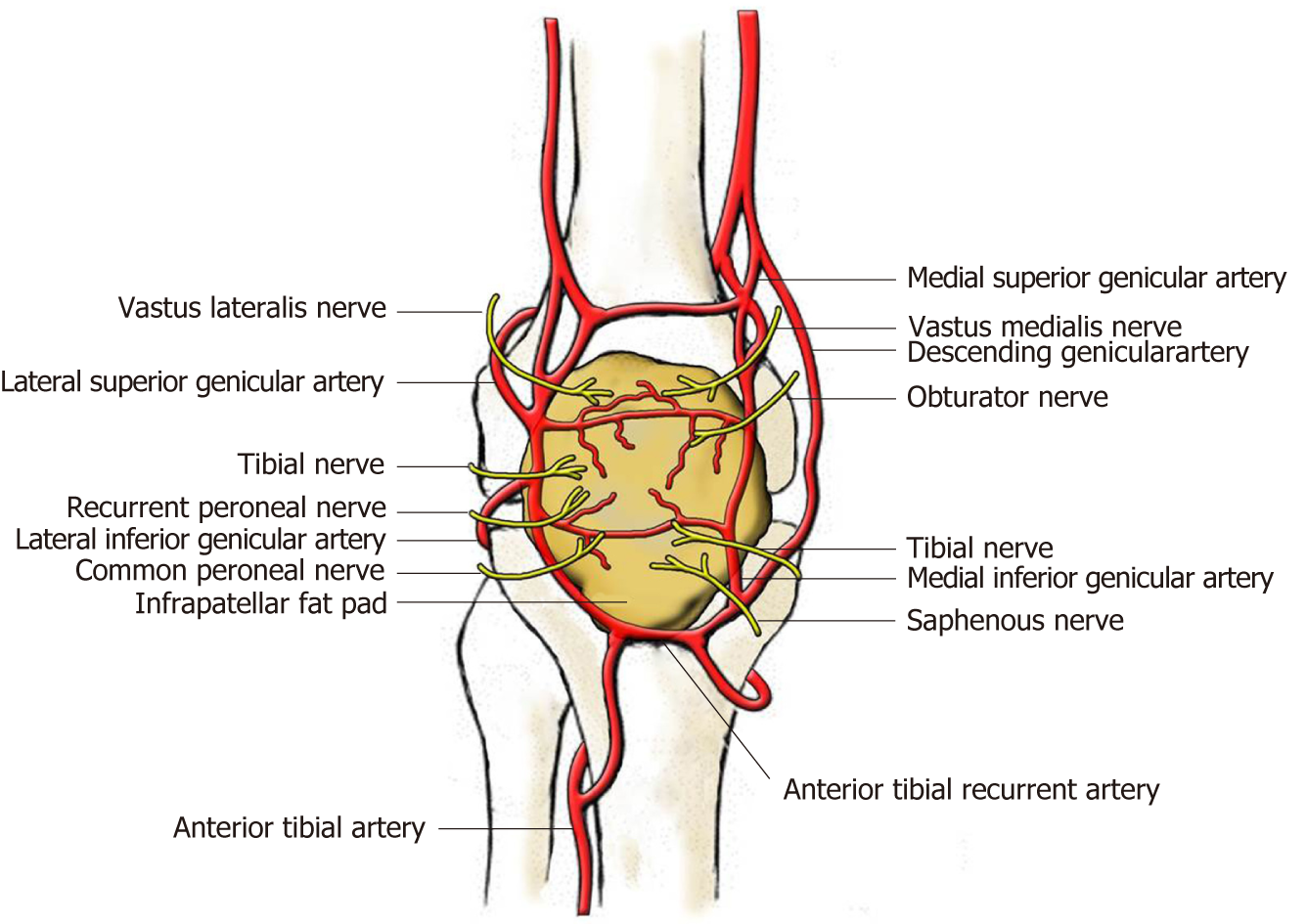
Suprapatellar fat pad impingement syndrome. Causes of Injury to the Infrapatellar Fat Pad. The infrapatellar fat pad IFP also known as Hoffas fat pad is an intracapsular extrasynovial structure that fills the anterior knee compartment and is richly vascularized and innervated. M794 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate.
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 BillableSpecific Code. Of these one of the most common is quadricepssuprapatellar fat-pad impingement syndrome which may be related to chronic microtrauma. Pain below the knee cap.
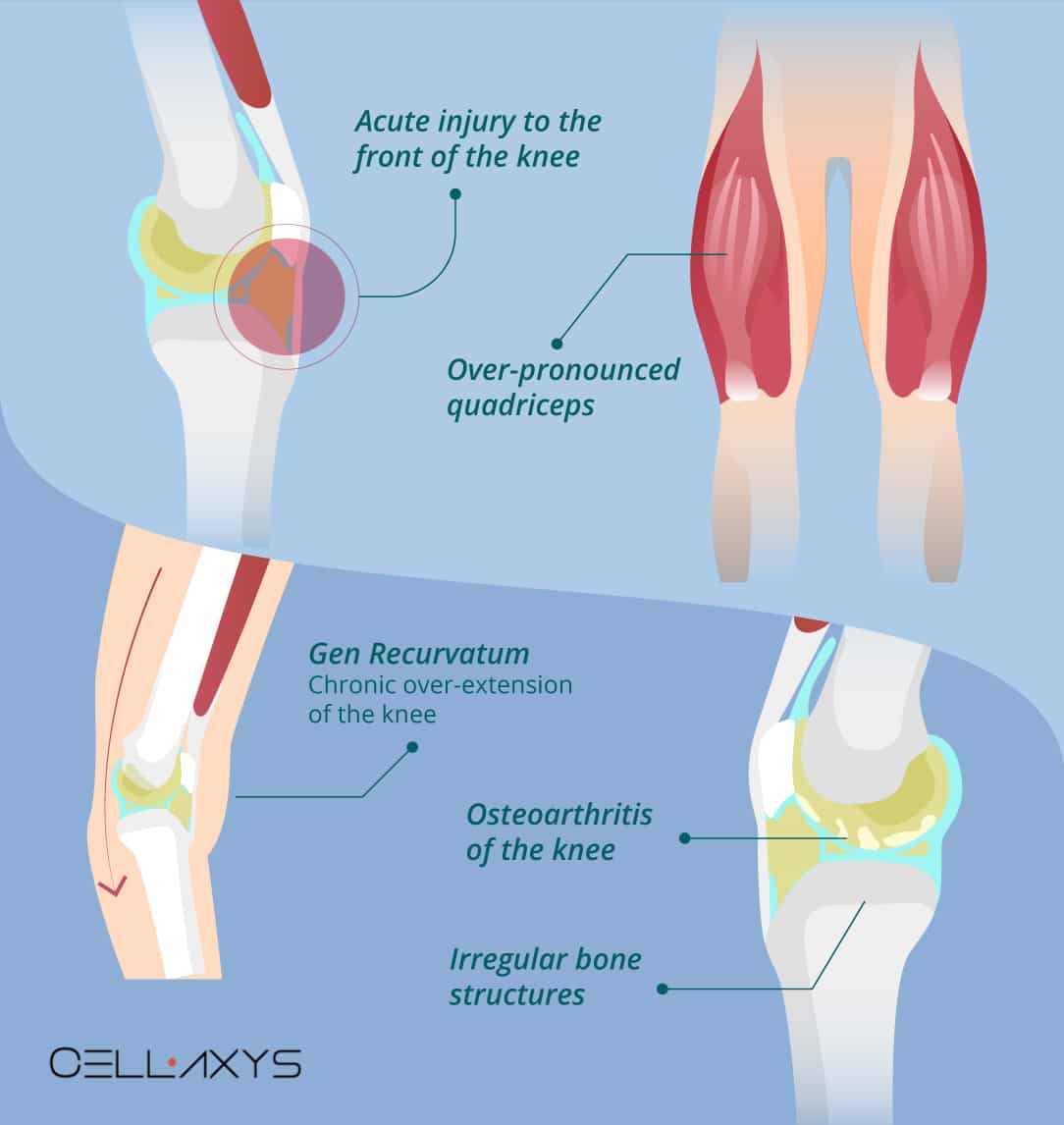
3 rows Edema of the suprapatellar fat pad is found in 12 to 14 of patients undergoing knee MR. Iliotibial band friction syndrome and greater trochanteric bursitis. It can be caused by a sudden injury such as a direct blow to your knee.
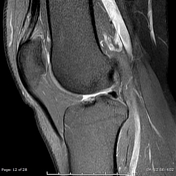
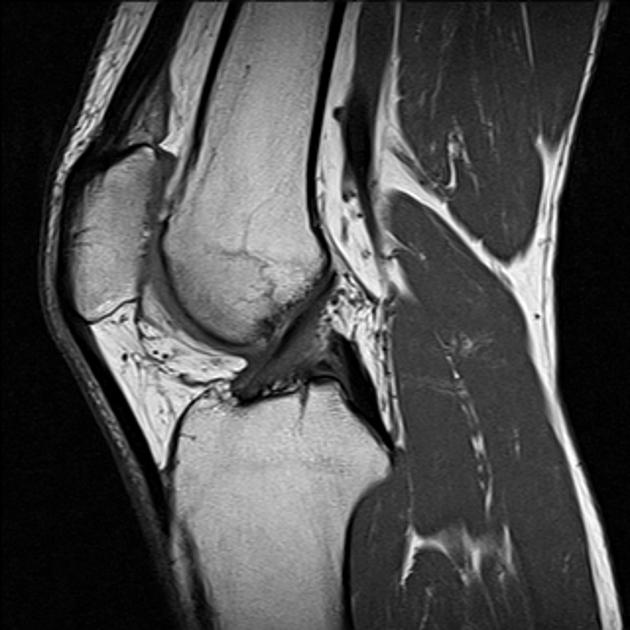
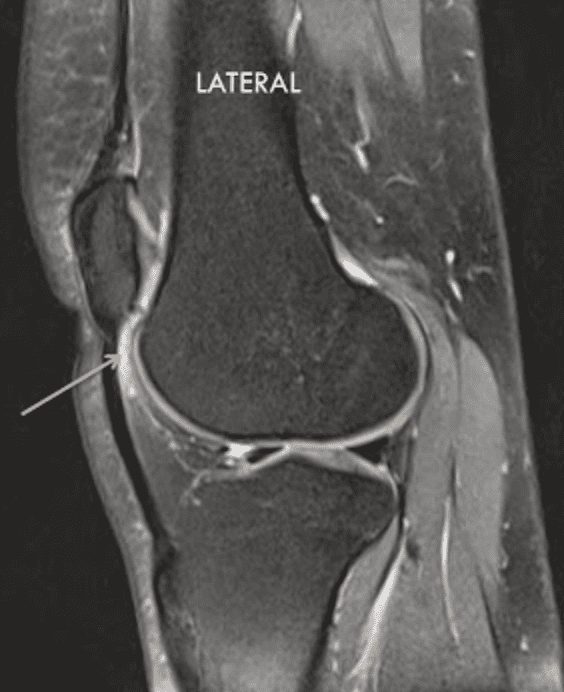
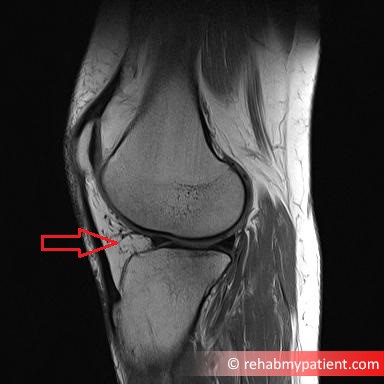
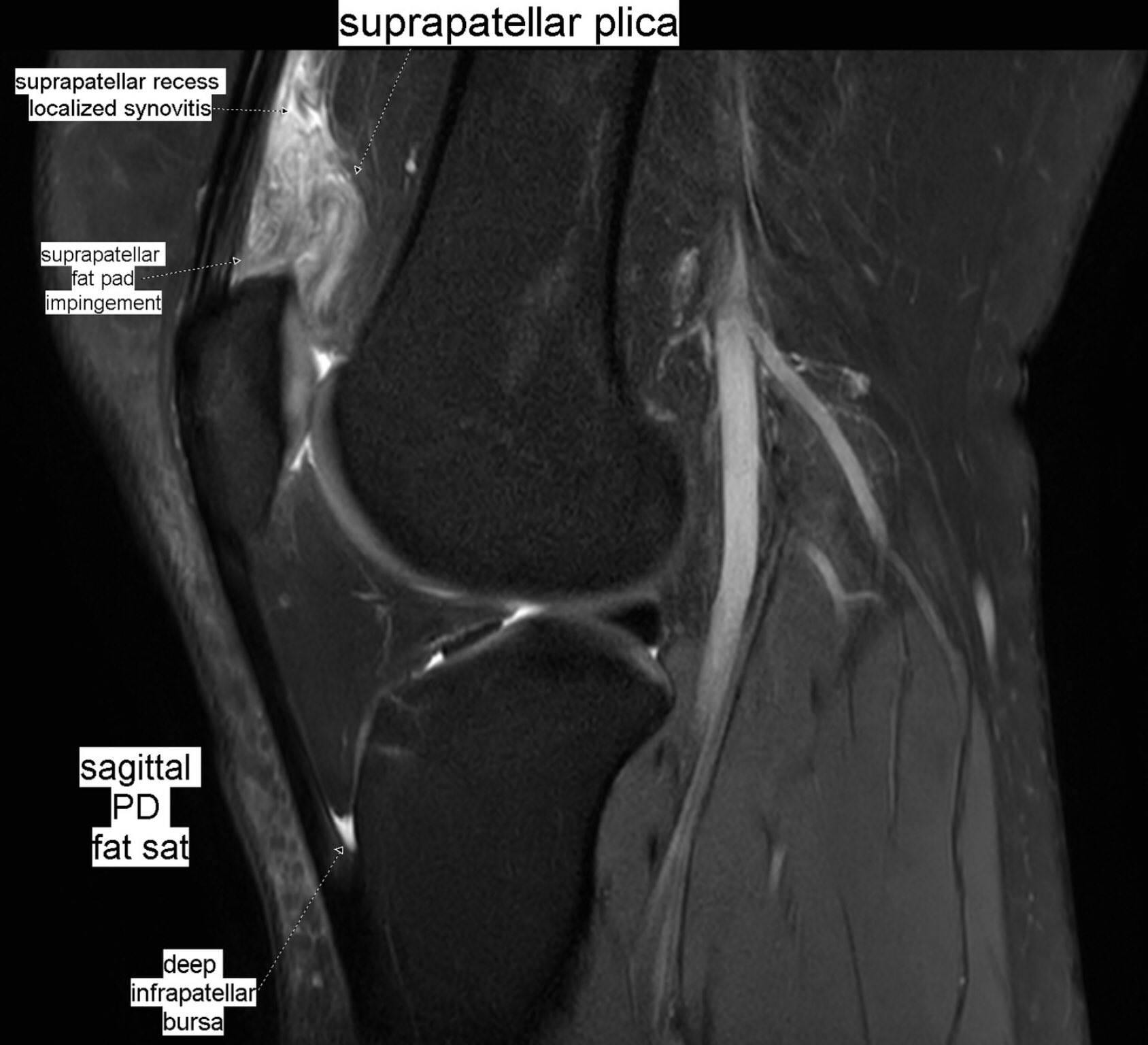
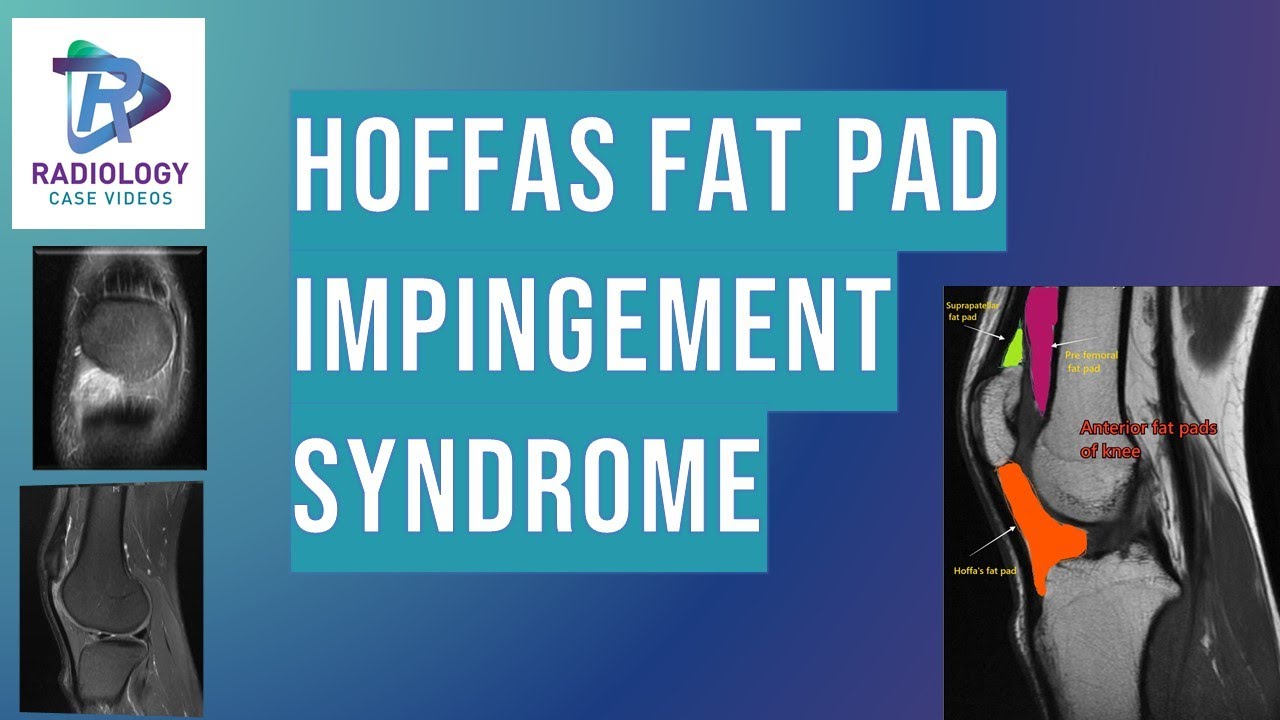
Hypertrophy of infrapatellar fat pad. Infrapatellar fat pad syndrome can happen for a number of reasons. In this syndrome the posterior border of the anterior suprapatellar quadriceps fat pad is high signal on PD MRI and convex with a mass effect upon the suprapatellar.
This video demonstrates manual therapy techniques for the patella and knee using the Motion Guidance Contact Pad. Front aspect knee pain. The term quadriceps fat-pad impingement has been used to describe an inflammatory process within the anterior suprapatellar fat manifested on MRI as high T2 signal low T1 signal and mass effect on the quadriceps tendon.
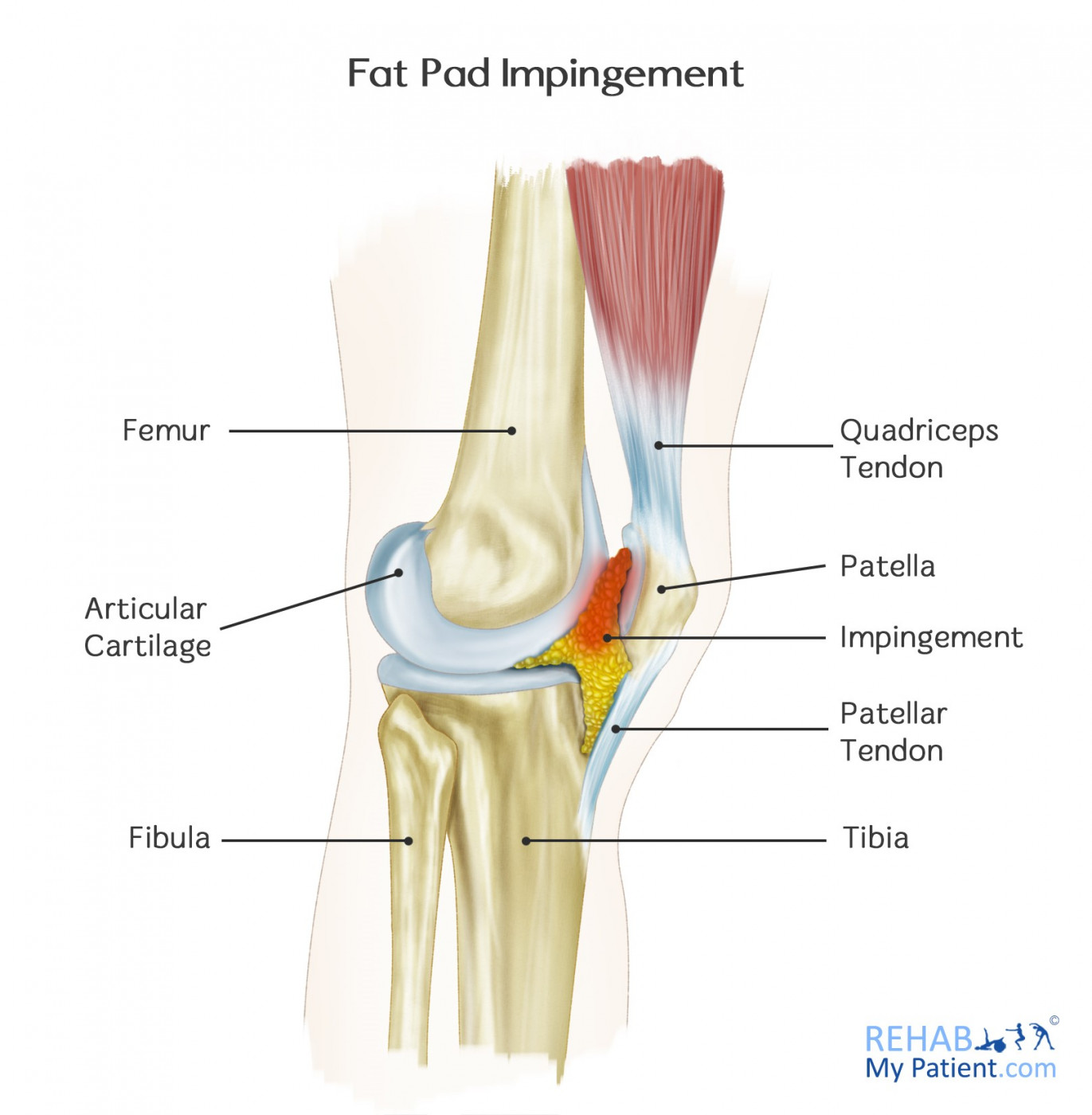
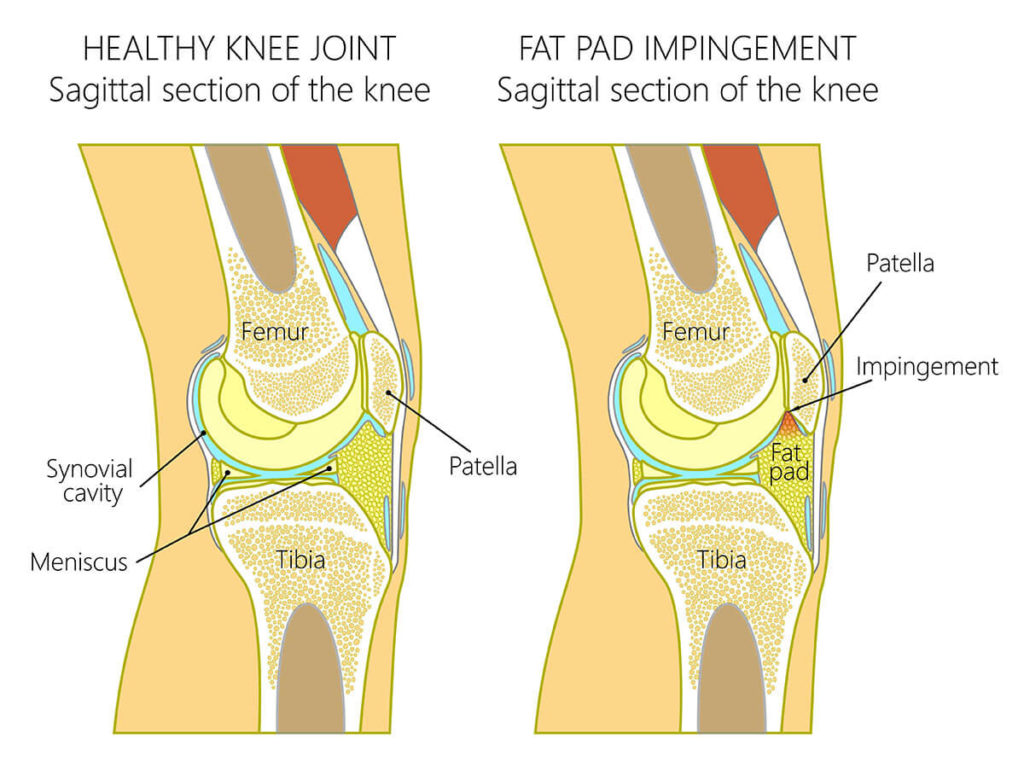
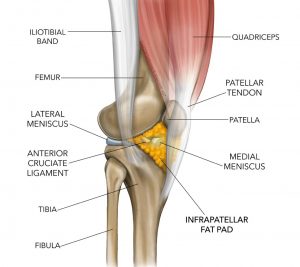
The suprapatellar fat pad prevents direct friction of the quadriceps tendon against the femoral condyle allowing for normal movement of the knee. This is a vicious cycle which is difficult to break. M794 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of hypertrophy of infrapatellar fat pad.
Once the fat pad swells it is more prone to further injury or impingement. Its degree of innervation the proportion of substance-P-containing fibres and close relationship to its posterior synovial lining implicates IFP pathologies as a source of infrapatellar knee pain.
Symptoms of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Syndrome.
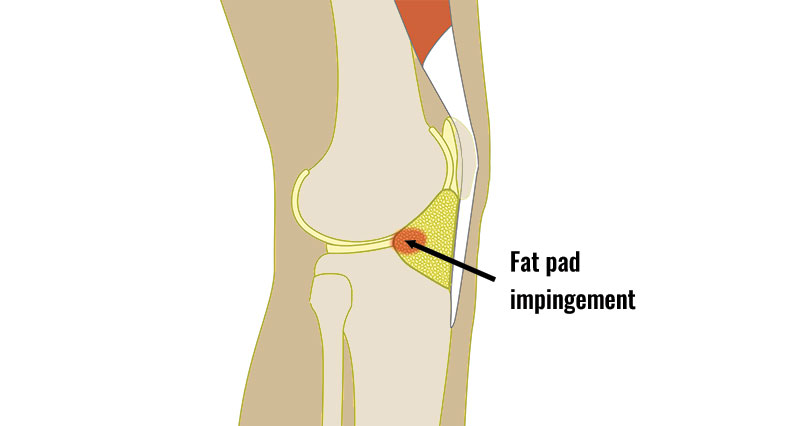
The term quadriceps fat-pad impingement has been used to describe an inflammatory process within the anterior suprapatellar fat manifested on MRI as high T2 signal low T1 signal and mass effect on the quadriceps tendon. Symptoms of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Syndrome include. In this syndrome the posterior border of the anterior suprapatellar quadriceps fat pad is high signal on PD MRI and convex with a mass effect upon the suprapatellar. Pain with leg strengthening exercises. In fat-pad impingement syndromes the etiologies are different for each knee fat pad. Pain below the knee cap. The fat pad can become inflamed if it is squashed between the femur and patella impinged or damaged which can occur as the result of direct trauma or repeated aggravating movements. Posterior cruciate ligament ruptures. Pain during kicking movements.
Swelling of the knee. Iliotibial band friction syndrome and greater trochanteric bursitis. More often though it develops gradually over time if you repeatedly over-extend your knee. Patellar tendonitis umpers knee Meniscal injuries. The fat pad can become inflamed if it is squashed between the femur and patella impinged or damaged which can occur as the result of direct trauma or repeated aggravating movements. This video demonstrates manual therapy techniques for the patella and knee using the Motion Guidance Contact Pad. This is a vicious cycle which is difficult to break.





























Post a Comment for "Suprapatellar Fat Pad Impingement Syndrome"